Was this page helpful?
Cluster Types - X Cloud and Standard¶
Overview¶
When creating a cluster, you can choose between a Standard or an X Cloud cluster.
X Cloud clusters offer up to 90% storage utilization, better elasticity, and faster scaling. Some ScyllaDB features are not available in X Cloud clusters. See X Cloud Limitations.
Standard clusters offer up to 70% storage utilization and a complete set of ScyllaDB features.
Standard |
X Cloud |
|
|---|---|---|
Tablets |
Yes (default) |
Yes (enforced) |
vNodes |
Yes |
No |
Storage Utilization |
Up to 70% |
Up to 90% |
Multi-DC |
Yes |
No |
Vector Search |
Yes |
Yes |
ScyllaDB Features |
Full |
Support for counters will be available soon |
X Cloud Clusters¶
If you choose the X Cloud option, the better tablets-based data replication in your cluster is enforced on all keyspaces. Owing to tablets, X Cloud clusters provide better elasticity, faster scaling, and allow you to reach up to 90% storage utilization.
Counters are not yet available in X Cloud clusters. We are actively working to add support for counters in an upcoming release.
X Cloud Auto Scaling¶
The serverless architecture behind X Cloud is designed to give you the speed, scalability, and cost control you need — without the operational burden. You always have the right level of performance at the right time, eliminating overprovisioning and underutilization. X Cloud eliminates manual scaling, capacity planning, and cluster rebalancing, freeing your team to focus on applications, not infrastructure.
X Cloud clusters scale automatically using different instance families and a mix of instance sizes, increasing or decreasing new instances as the storage grows or drops. This brings multiple benefits to the scaling process.
You avoid overprovisioning. The cluster capacity is automatically adjusted to match real-time demand.
It enables up to 90% storage utilization, allowing you to maintain reliable performance at the lowest possible cost.
Scaling is faster. Due to the tablets-based replication architecture, new nodes can be added in parallel and almost instantly balance the load.
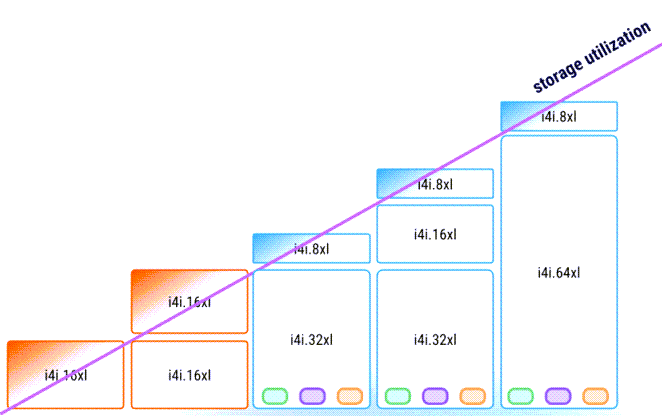
X Cloud clusters are auto-scaled within one predefined instance family, but with different instance types to ensure optimal storage utilization. See Scaling Policy for details.
Auto Scaling Policy¶
When you create an X Cloud cluster, you can define an initial auto-scaling policy. You can update that policy later as needed.
To define the initial auto-scaling policy when creating a new cluster, configure the options in Data Center Scaling Policy.
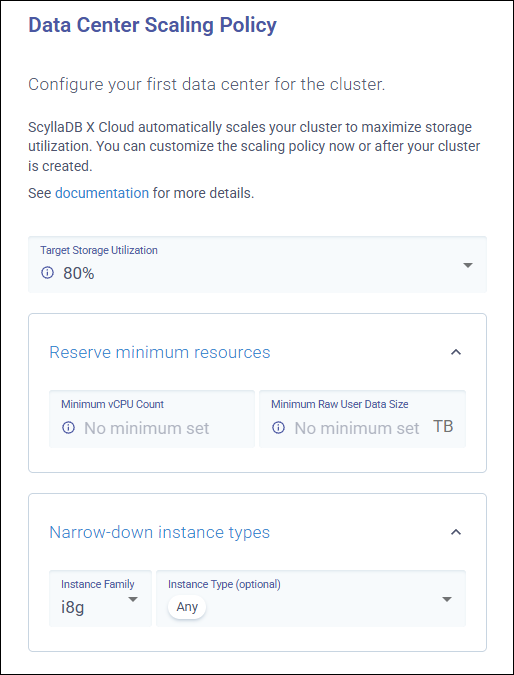
Target Storage Utilization - Specifies the storage utilization you want to maintain. ScyllaDB will be performing auto-scaling operations with the goal of maintaining the storage utilization level specified by this option.
The default is 80%.
The maximum is 90%.
You should adjust the value depending on the workload. For workloads with a high volume of write operations, we recommend values lower than 85 to ensure that the ScyllaDB Cloud will be able to scale the cluster. If the storage utilization is set too high the cluster will scale later and might throtle the operations.
The Minimum vCPU Count and Minimum Raw User Data Size options allow you to reserve minimum respurces for your cluster:
Minimum vCPU Count - Specifies the minimum number of vCPUs to reserve compute capacity for that particular cluster. You can customize it depending on the initial load you anticipate for your cluster. If set, ScyllaDB Cloud will never scale the cluster below this vCPU count, even during automatic downscaling operations. By default, no minimum vCPU count is set.
Minimum Raw User Data Size - Specifies the minimum physical storage capacity. You can customize it depending on the initial load you anticipate for your cluster. If set, ScyllaDB Cloud will never scale the cluster below this capacity, even if storage is underutilized. Automatic downscaling operations will respect this minimum. By default, no minimum size is set.
The Instance Family and Instance Type options allow you to narrow down the instances to be used for auto-scaling:
Instance Family - Specifies the instance family to be used for auto-scaling. X Cloud clusters are scaled automaticaly within one predefined instance family.
Instance Type - Specifies instance types to be used for auto-scaling. By default, all instance types within a given family can be used when auto-scaling a cluster to optimize storage utilization and compute.
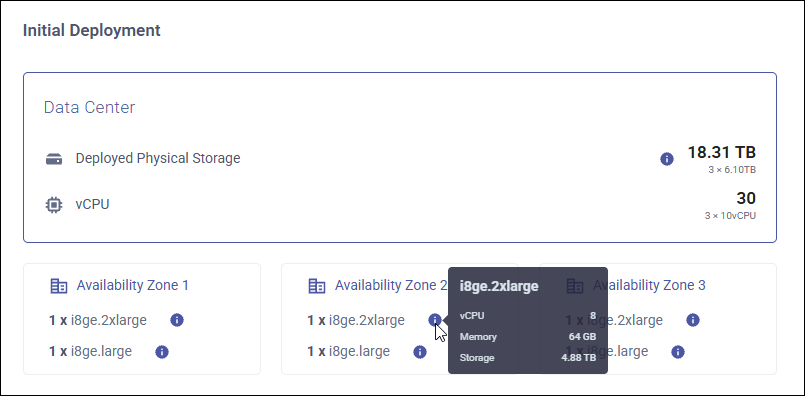
After you customize the auto-scaling policy, the Initial Deployment summary will show:
Deployed Physical Storage - The total initial amount of physical storage allocated to all nodes in the cluster.
vCPU - The number of vCPUs.
The availability zones with the instance type configuration for each zone. The cluster consists of 3 identical zones, automatically replicated.
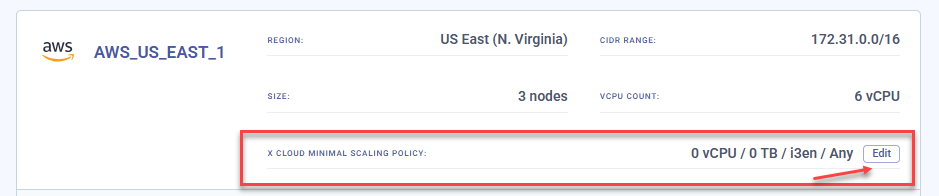
To modify the auto-scaling policy for an existing cluster, go to your cluster’s page and click Edit Scaling Policy.
Replication Factor (RF)¶
When using certain ScyllaDB features, the RF must be set to match the number of racks in ScyllaDB Cloud. ScyllaDB Cloud is configured with three racks, so the RF should be set to 3 when you use these features.
The features that require this configuration are:
Materialized Views (MV)
Secondary Indexes (SI)
Alternator
CDC
X Cloud Limitations¶
X Cloud clusters use tablet-based data distribution. Counters are not yet supported for tablets, and therefore are currently unavailable in X Cloud clusters. If you have to use counters, create a Standard cluster and disable tablets.
In addition, X Cloud doesn’t support multi-datacenter (multi-DC) deployments.
We are actively working to remove these constraints in an upcoming release.
Standard Clusters¶
If you choose the Standard option, data replication in your cluster can be based on tablets (default) or vnodes, depending on the configuration of your keyspaces.
When you CREATE a keyspace, it has tablets enabled by default. To use vnodes-based data replication, you must explicitly disable tablets when you CREATE a keyspace. See Enabling Tablets in the ScyllaDB documentation for instructions.
You need to disable tablets in favor of vnodes if you’re going to use couters. See Limitations.
A Standard cluster allows you to reach up to 70% storage utilization.
References¶
See Data Distribution with Tablets in the ScyllaDB documentation for more information about tablets.
