Was this page helpful?
ScyllaDB Cloud Security Concepts¶
This article provides a high-level description of the ScyllaDB Cloud security mechanism.
Overview¶
ScyllaDB Cloud security is built on four principles:
Principle of Least Privilege
Isolation
Auditing
Encryption
The following sections describe how these principles are used across different aspects of ScyllaDB Cloud. Everything below refers to both customer accounts (BYOA) and ScyllaDB accounts unless explicitly stated otherwise.
Terms¶
Control Plane: ScyllaDB Cloud backend, a collection of services and servers that manage ScyllaDB Cloud users, ScyllaDB Cloud application (site), manage and monitor all the ScyllaDB database clusters.
ScyllaDB Cluster: ScyllaDB servers running in either a ScyllaDB account or the customer account (BYOA), including ScyllaDB nodes, ScyllaDB Manager, and ScyllaDB Monitoring servers.
Topology¶
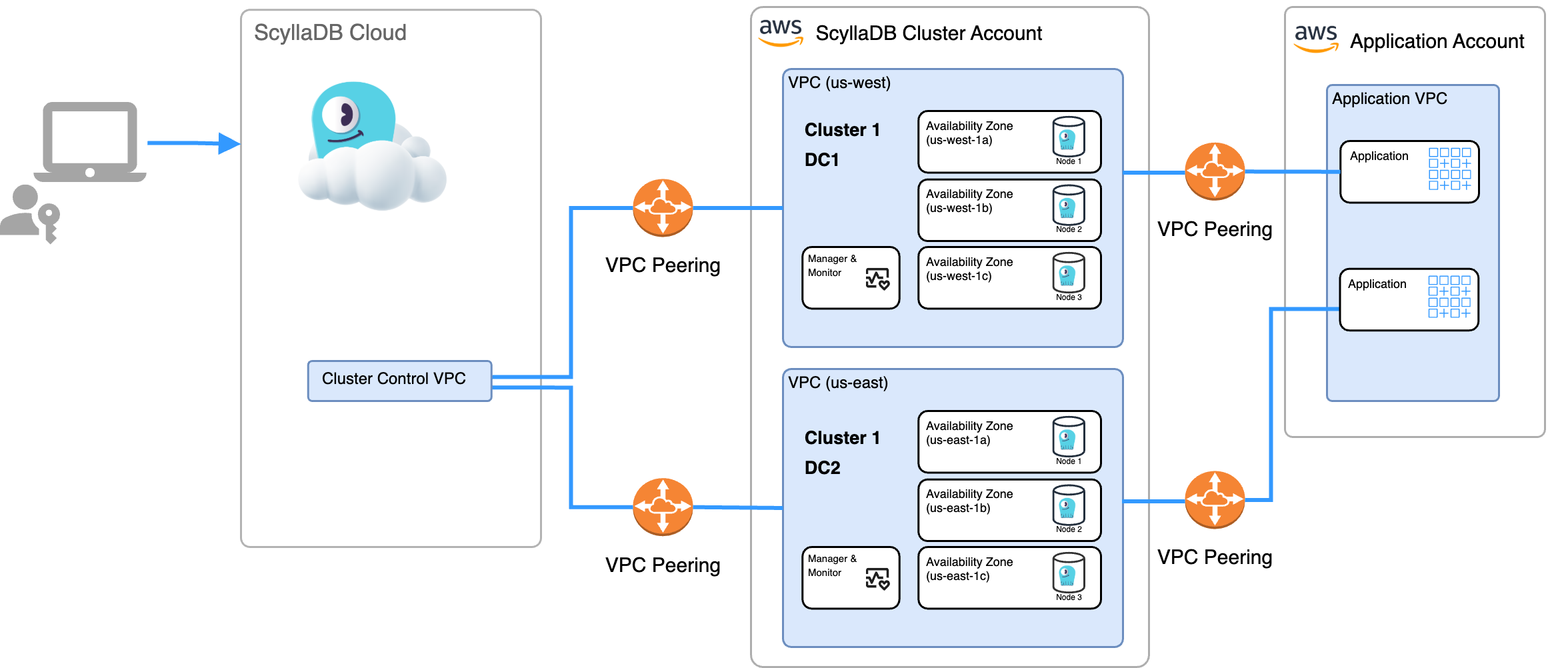
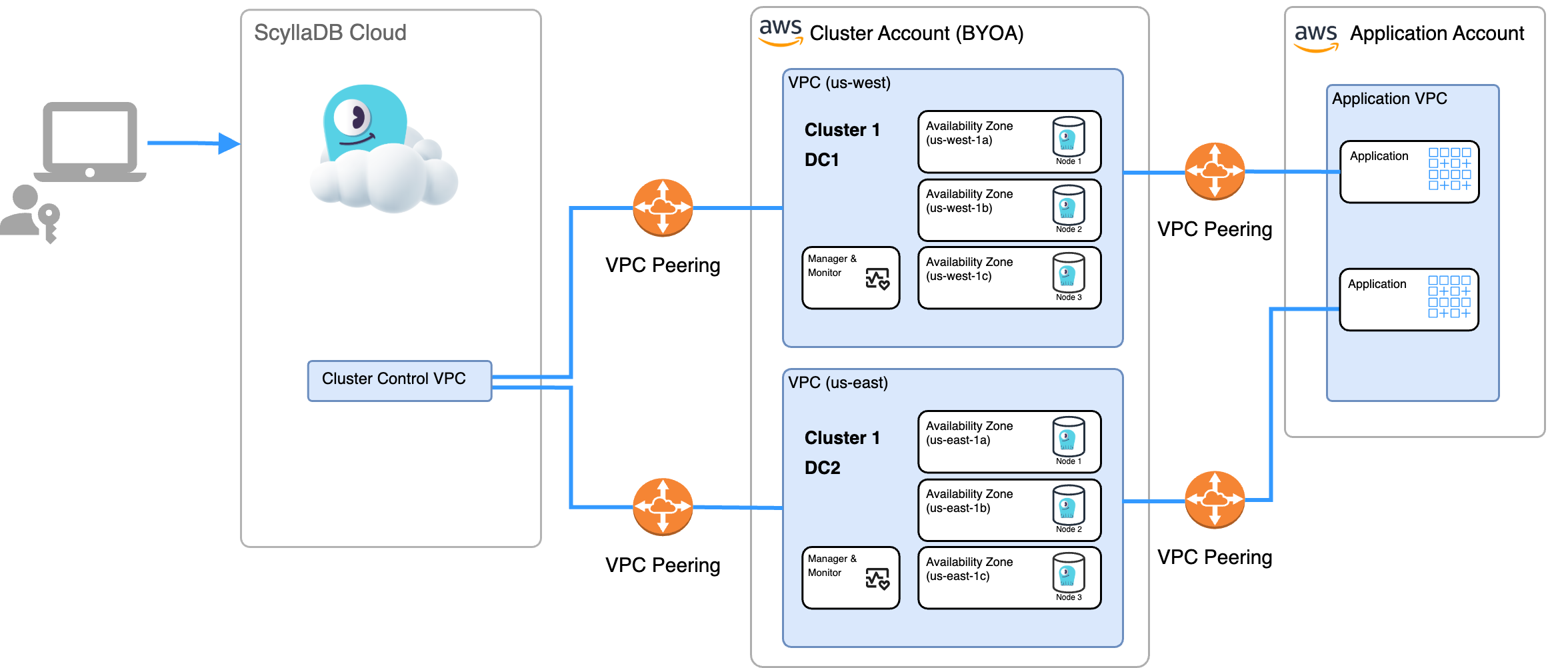
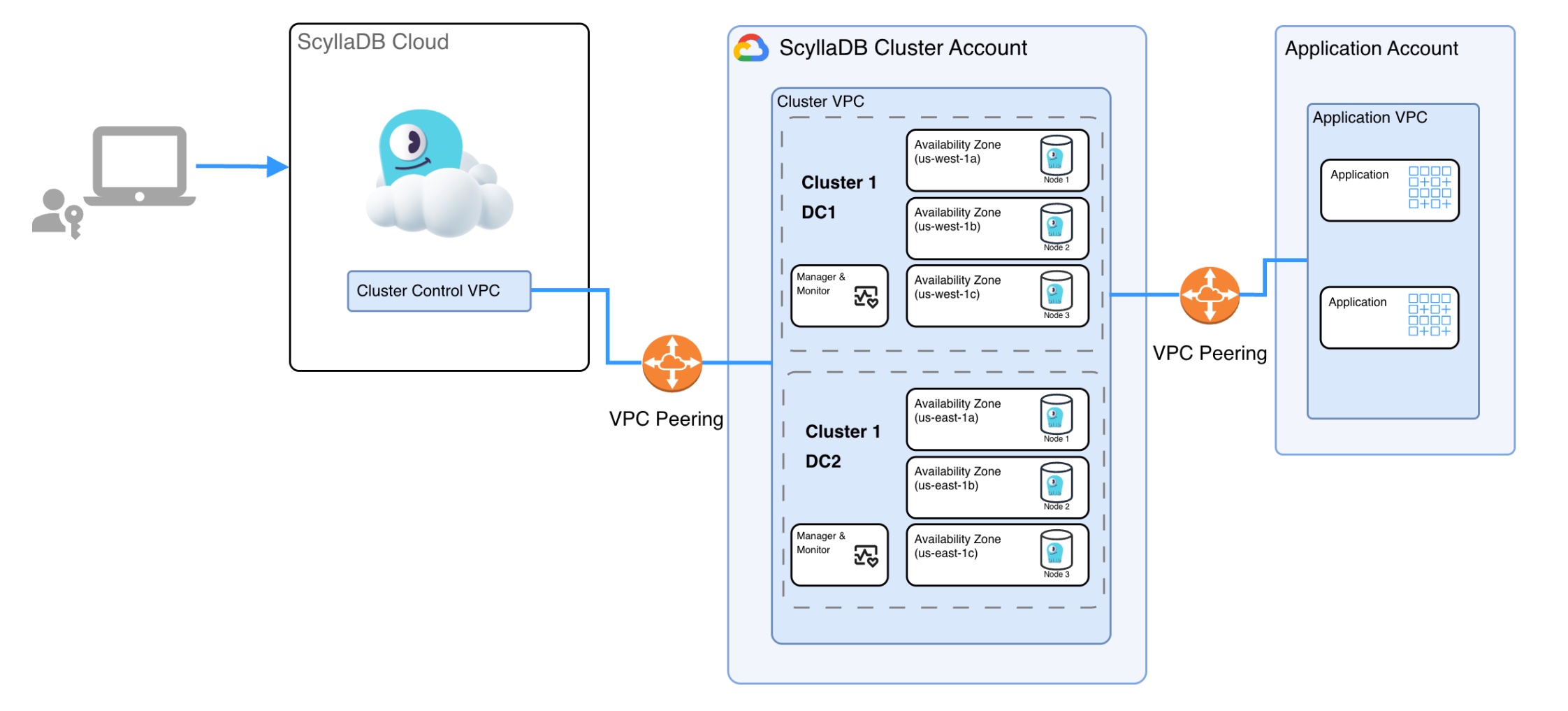
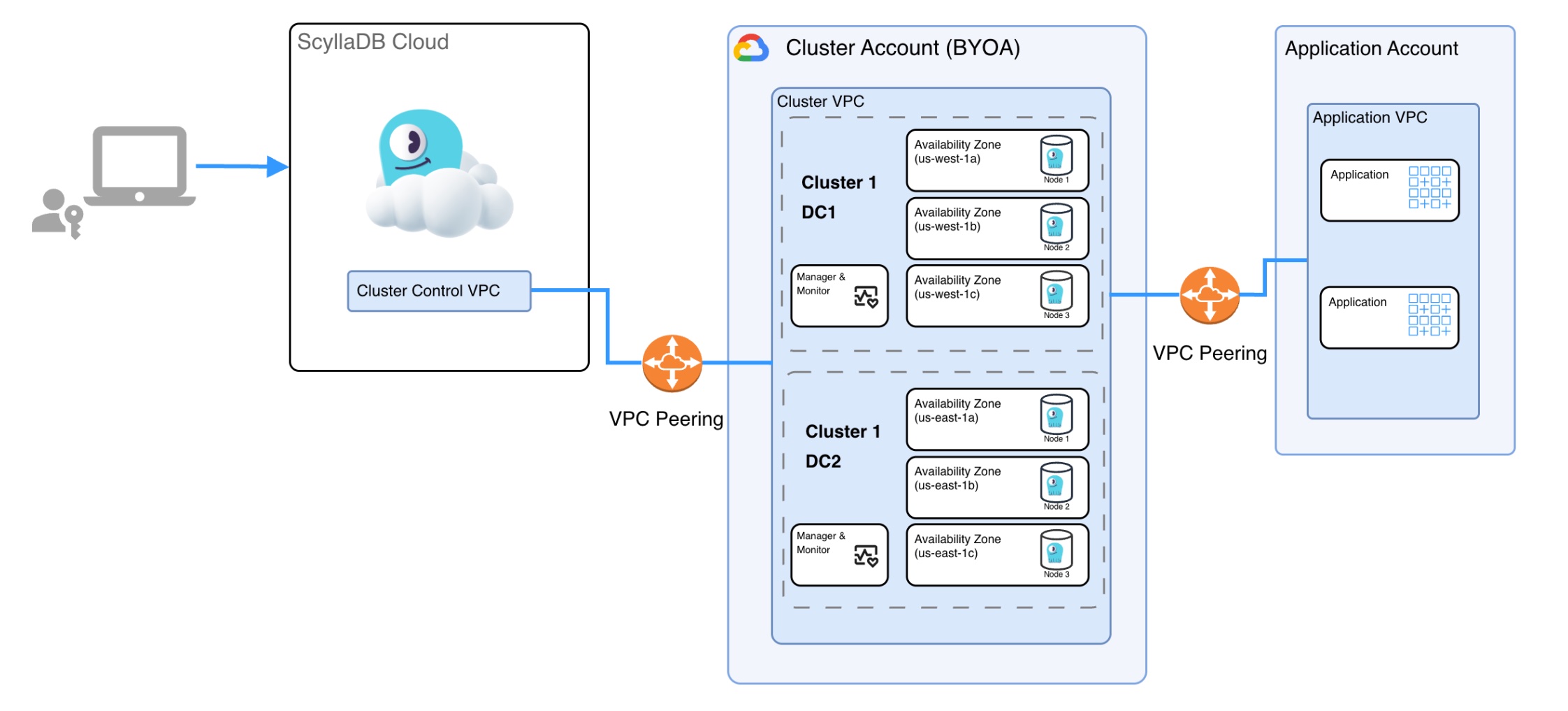
Each ScyllaDB cluster is running on a dedicated, isolated environment, including:
Dedicated VPC
Dedicated VMs for the ScyllaDB database
Dedicated VMs for ScyllaDB Monitoring and ScyllaDB Manager servers
The diagrams below describe the topology of a managed ScyllaDB Cloud cluster in a ScyllaDB account or customer account (BYOA).
ScyllaDB Cloud on AWS Architecture - ScyllaDB Account
ScyllaDB Cloud on AWS Architecture - BYOA
ScyllaDB Cloud on GCP Architecture - ScyllaDB Account
ScyllaDB Cloud on GCP Architecture - BYOA
Isolation Invariants¶
There is no access from one cluster to another.
Customer data is limited to the ScyllaDB cluster. The Control Plane does not store, query, or access the customer data.
The Control Plane access to ScyllaDB clusters is limited to:
Monitoring information (metrics).
Operations, such as adding nodes, upgrading, etc.
Each cluster manages its own S3 backup bucket per DC (region).
Principle of Least Privilege Invariants¶
All the access points between elements are closed by default. Relevant connections and API are explicitly enabled.
ScyllaDB database users can only access their ScyllaDB database over CQL or REST API (Alternator).
Users can not log in to ScyllaDB nodes, Monitoring, or Manager servers; using an IP/port whitelist is enforced.
ScyllaDB Monitoring can only access ScyllaDB database servers monitoring and log collection APIs; using an IP/port whitelist is enforced.
ScyllaDB Manager can only access ScyllaDB database servers Manager Agent API; using an IP/port whitelist is enforced.
Access to the backup stored on S3 (AWS) and Cloud Storage (GCP) is limited to the ScyllaDB cluster instances. Note that if a cluster is destroyed, ScyllaDB Cloud must access the backup to restore the cluster.
Access Control¶
ScyllaDB Cloud technical support engineers can securely access our cloud infrastructure to resolve incidents or customer requests. We adhere to all security practices:
Limited Access: Only a designated subset of technical support engineers can access the production infrastructure, and access is limited through the Internal Security Gateway.
Audited Access: Each session is logged for audit, including the history of the commands and results.
Access Supervision: Customers can request to supervise our engineers in real-time during the planned support. However, this approach is not feasible for timely interventions.
Encryption¶
Encryption At Transit¶
All data in transit is encrypted:
ScyllaDB Node-to-Node in the same region - using AWS VPC Encryption in transit or GCP VPC Encryption in transit.
ScyllaDB Node-to-Node between regions - All data flowing across regions over the AWS or GCP global network is automatically encrypted at the physical layer before it leaves AWS- or GCP-secured facilities. All traffic between AZs is encrypted.
ScyllaDB Client-to-Node - enabled for all new clusters in ScyllaDB. The client application must be configured to enable encrypted connections. See Client-to-node Encryption.
Storage Level Encryption - AWS¶
Storage-level encryption is a variant of encryption at rest. Encrypting data stored on a storage level protects it from unauthorized access.
ScyllaDB Cluster uses NVMe to store information. The data on NVMe instance storage is encrypted using an XTS-AES-256 block cipher implemented in a hardware module on the instance. The encryption keys are managed by EC2 and generated using the hardware module and are unique to each NVMe instance storage device.
Storage Level Encryption - GCP¶
ScyllaDB Cluster uses SSD to store information. Compute Engine automatically encrypts your data when it is written to local SSD storage space.
Database-level Encryption¶
Database-level encryption is a method of encrypting all data before it is stored in the database. In ScyllaDB Cloud, database-level encryption is extended with Customer Managed Keys (CMK) encryption control. This ensures that data is securely stored and the customer manages the key. The keys are stored and protected separately from the database; see separating privileges.
